Members of the Charter
News
20 March 2020
Members of the Charter
The International Charter "Space and Major Disasters" is a worldwide collaboration of space agencies and space system operators that work together to provide satellite data for disaster management.
Three space agencies founded the Disasters Charter in 2000, but this international venture has grown considerably in the 20 years since. Today, the Disasters Charter consists of 17 members, who together contribute data from 61 satellites.
Each member makes a commitment when they join to provide satellite data at no charge to users. Working together, the members provide a 24 hours a day, 7 days a week service through a single access point, which has been operational since November 1st, 2000.
Who are our members, and what do they contribute to the Disasters Charter?

Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES)
Founded in 1961, the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES) is the government agency responsible for shaping and implementing France's space policy in Europe.
Its task is to invent the space systems of the future, bring space technologies to maturity and guarantee France's independent access to space. CNES is a pivotal player in Europe's space programme, and a major source of initiatives and proposals that aim to maintain France and Europe's competitive edge. It conceives and executes space programmes with its partners in the scientific community and industry, and is closely involved in many international cooperation programmes—the key to any far-reaching space policy.
Through its ability to innovate and its forward-looking vision, CNES is helping to foster new technologies that will benefit society as a whole, covering five main areas - Launchers, Sciences, Earth Observation, Telecommunications and Navigation as well as Defence and Security.
CNES supplies imagery from the Pleiades and the SPOT-6 and 7 satellites. In 2019, 39% of the damage-assessment maps compiled from Charter members' satellites were generated using imagery from Pleiades, whose agility and responsiveness need no confirmation.
CNES last performed chairmanship of the Disasters Charter from October 2018 to April 2019 for the sixth time.
European Space Agency (ESA)
The European Space Agency (ESA) is an international organisation with 22 member states that was formed in 1975. It is dedicated to providing and promoting cooperation in space research, space technology and their applications in a range of domains including space exploration, launchers, telecommunications and Earth Observation (EO). In the domain of EO the agency develops and operates space missions, has EO programmes in different areas from Science to Applications, is responsible for the Copernicus Space Component on behalf of the European Commission, and participates in international collaborations such as GEO, CEOS and including the International Charter ‘Space & Major Disasters'.
ESA was one of the founding members of the Charter in 1999. Since its inception ESA has conducted the role of Primus Inter Pares a total of six times, the last one being over the period from October 2017 to April 2018. ESA contributes in the Charter with the Copernicus Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2 and Proba-V missions and also by providing the 24/7 On Duty Officers (ODO) for the reception of calls for activation, Emergency on-Call Officers (ECO) on a weekly rotation with other Charter members and on a best effort basis Project Managers (PM) responsible for Charter activations. Furthermore, ESA has developed and operates the data workflow management system called Charter Operations System (COS) that is the backbone of its operations on an emergency basis with the Charter operational staff and its partners and Authorised Users during activations.
Canadian Space Agency (CSA)
Established in March 1989, the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) is a federal agency responsible for managing all of Canada's civil space-related activities. It focuses its activities and resources on three main areas:
- Space exploration: Participation in astronaut missions, astronomy and planetary studies, scientific research in space (execution and support).
- Space utilization: Earth observation by satellite and collection of space data.
- Space science and technology: Development of innovative space technologies and applications used on Earth.
Since becoming a founding member of the Disasters Charter in 2000, the CSA has been providing data from its RADARSAT satellites to support relief efforts around the world. RADARSAT-1 operated until 2013 and contributed to relief operations in 244 disaster events. It was succeeded by RADARSAT-2, which is still in good working order after more than a decade in orbit. The RADARSAT Constellation Mission (RCM), the evolution of the RADARSAT program and Canada's newest Earth observation satellite, was launched in June 2019 and will soon begin supplying data to assist search and rescue teams all over the world. The CSA performed chairmanship of the Charter six times, including hosting Charter meetings.
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), founded in 1970, is a scientific agency in the United States. It is responsible for monitoring and observing Earth systems with instruments and data collection networks, to understand and describe Earth systems through research and analysis of that data. NOAA's Satellite Office provides secure and timely access to global environmental data and information from satellites and other sources to promote and protect the Nation's security, environment, economy, and quality of life. NOAA became a member of the Charter in 2001, and makes available the data from their geostationary and polar orbiting fleets.
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
The government of India established the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in 1969 with a vision to "harness space technology for national development while pursuing space science research & planetary exploration". ISRO provides space technology based solutions to actively support the disaster management activities of the Central/State Government agencies in the country, such as the Ministry of Home Affairs, National Disaster Management Authority and State Disasters Management Departments.
ISRO joined the International Charter in 2001 and has been contributing significantly to major disasters across the world, through its fleet of IRS series of satellites, such as, IRS-1C, 1D, P4, IMS-1, Resourcesat-1, 2, 2A, Cartosat-1, 2, 2E, Oceansat-2 and RISAT-1 (Microwave remote sensing satellite). Also, ISRO took up the Charter Lead responsibility during 2002, 2005, 2009 and 2015. During these times, ISRO played a key role in all responsibilities, as the lead, and effectively coordinated all the disaster management events, as stipulated for the Charter activations. ISRO has again proposed to take up the responsibility as Lead during 2021.
Comisión Nacional de Actividades Espaciales (CONAE)
Argentina's National Commission on Space Activities (CONAE) was created by government decree in 1991. Today the Argentine Space Agency designs, executes, and administers Argentina's space programme, which includes the SAC (Satelite de Aplicationes Cientificas) series of satellites, as well as tracking, telemetry and control ground stations on its territory. Research and development are also part of CONAE's mandate. In addition, CONAE provides satellite imagery over Argentina and other southern latitudes.
CONAE joined the Disasters Charter in 2003.
Russian State Space Corporation (ROSCOSMOS)
The Russian State Space Corporation (ROSCOSMOS) is responsible for the implementation of the Russian state Space Program, state administration and management of space activities in Russia aimed to improve the social and economic development of Russia. It works on the creation and use of Russian space assets and implements international cooperation in the exploration and use of outer space.
ROSCOSMOS joined the Disasters Charter in August 2013 and provides their Earth remote sensing satellites for operational monitoring of natural and technological major disasters in Russia and worldwide for the benefit of the Russian Emergency Ministry (EMERCOM) and the Charter members, Charter Authorised Users (AU) and partners.
Since accession to the Charter, ROSCOSMOS has participated in more than 170 Charter activations and provided more than 62 million square kilometers of satellite data over more than 30 countries (as of 2019).
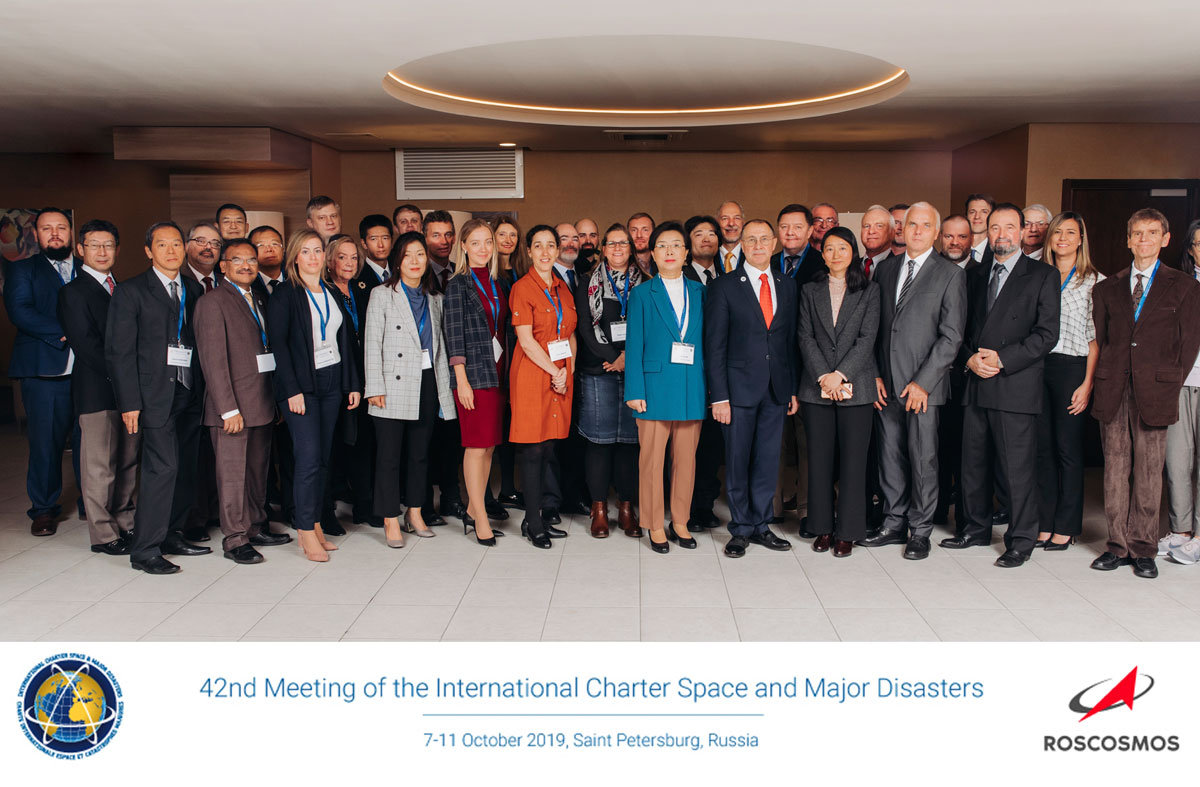
ROSCOSMOS hosted the Charter Board meetings and chaired the Charter in 2016 and 2019.
United States Geological Survey (USGS)
The US Geological Survey (USGS) was created by an act of the US Congress in 1879. USGS is the sole science agency for the Department of the Interior and is sought out by thousands of partners and customers for its natural science expertise and its vast earth and biological data holdings. In addition, USGS takes a lead role in the operation, collection, and application of Earth Observation (EO) satellite data. The agency is responsible for operating the Landsat satellites which have been collecting EO data since 1972, providing a continuous global record of the Earth's land surface and holding the largest archive of remotely sensed land data in the world.
In 2005, USGS became an International Charter member. Since that time, they have acted in the lead role on 3 occasions; 2006, 2010, and 2015. The USGS currently offers visible satellite data from the Landsat 8 (OLI/TIRS) and Landsat 7 (ETM+) satellites in addition to very high-resolution imagery on behalf of several US-based commercial sources (DigitalGlobe WorldView/GeoEye and PLANET). Throughout their involvement in the Charter, USGS has provided over 100,000 individual scenes for use by emergency managers.
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA)
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) was born in 2003 through the merger of three aerospace related institutions and is designated as the core agency to support the Japanese government's overall aerospace development and utilization.
JAXA became a Charter member in 2005. The agency first contributed to the Disasters Charter with the Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS) "DAICHI" (2006 - 2011) and currently contributes with ALOS-2 "DAICHI-2" (launched in 2014) carrying the synthetic aperture radar PALSAR-2. JAXA plans to launch two additional EO satellites, ALOS-3 with an optical sensor and ALOS-4 with a radar sensor.
JAXA chaired the Charter in 2007 and 2012 and is planning to do so again this year. Another contribution by JAXA to the disaster management community is "Sentinel Asia", an initiative proposed at the Asia-Pacific Regional Space Agency Forum (APRSAF) in 2005 for disaster management support in the Asia-Pacific region. JAXA coordinates the interface between Sentinel Asia and the Charter, realizing the "escalation procedure" from Sentinel Asia members to the Charter in case of major disasters in this region.
UK Space Agency
The UK Space Agency is responsible for all strategic decisions on the UK civil space programme and provides a clear, single voice for UK space ambitions. At the heart of UK efforts to explore and benefit from space, the agency is responsible for ensuring that the UK retains and grows a strategic capability in space-based systems, technologies, science and applications. The agency leads the UK's civil space programme in order to win sustainable economic growth, secure new scientific knowledge and provide benefit to all citizens.
China National Space Administration (CNSA)
China National Space Administration (CNSA) was established in 1993, and is the governmental organisation of the People's Republic of China responsible for the management of space activities for civilian use and international space cooperation with other countries, and performs the corresponding governmental functions.
CNSA joined the Disasters Charter in 2007 and offers imagery from the FengYun-3C mission, and the Gaofen series (currently consisting of four satellites).
German Aerospace Center (DLR)
The German Aerospace Center DLR is Germany's national research center for aeronautics and space. As Germany's Space Agency, the German federal government has given DLR responsibility for the forward planning and implementation of the German space program as well as international representation of Germany's interests. DLR's research portfolio ranges from fundamental research in the fields of aeronautics, space, transportation and energy to innovative development of the applications and products of tomorrow. The Center for Satellite Based Crisis Information (ZKI) has particular expertise in the rapid provision, processing and analysis of satellite imagery during natural disasters and civil security issues worldwide.
DLR joined the Disasters Charter in 2010 and offers data from two satellites:
TerraSAR-X, Germany's first national remote sensing satellite implemented in a public-private partnership between DLR and Airbus (former EADS Astrium GmbH), was launched in June 2007 to create high-quality radar images of the Earth's surface. Its primary payload is an X-band radar sensor with a range of different modes of operation, offering space-based observation capabilities that were previously unavailable. In June 2010, TerraSAR-X was joined by its twin satellite, TanDEM-X. Flying in close formation only a few hundred meters apart, the two satellites simultaneously image the terrain below them, from different angles.
Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI)
The Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI) is a specialized institution founded for research and development of aircraft, satellites, and space launch vehicles ensuring the successful realization of the national space programs in Korea. KARI is leading the space development in Korea by developing the high-resolution Earth observation KOMPSAT series, Geo-stationary GK 2A/B, Compact Advanced Satellite (CAS) 500 series and Korea Space Launch Vehicle (KSLV). Despite its relatively short history, KARI has been carrying out assignments successfully and leading the world's aerospace scientific technology development.
KARI will further contribute to the creation of innovative achievements in space technology driving the fourth industrial revolution and improving the quality of life for the world. The National Satellite Operation and Application Center under KARI is dedicated to the operation of governmental Earth observation satellites, to process and distribute data and to support their applications in public and private sectors.
Since 2011, as a member of the Disasters Charter, KARI has been providing very high resolution optical and SAR data, collected by the KOMPSAT satellites. KARI has provided over 500 scenes of standard products for approximately 40 activations annually for rapid monitoring of global major disasters. KARI hosted the Board meeting and chaired the Disasters Charter in 2014, and is planning to take the chair again in 2022.
Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais (INPE)
The National Institute for Space Research in Brazil aims to serve as a national and international reference in both space and Earth environments, fostering knowledge and attending and anticipating demands of the Brazilian society.
INPE joined the Disasters Charter in 2011 and offers imagery from the CBERS-4 satellite, part of the co-operative CBERS (China-Brazil Earth Resources Satellite) program.
European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT)
EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites) is a global operational satellite agency at the heart of Europe. EUMETSAT's purpose is to gather accurate and reliable satellite data on weather, climate and the environment around the clock, and to deliver them to the National Meteorological Services of EUMETSAT's Member States in Europe, to the agency's international partners, and to users world-wide.
EUMETSAT joined the International Charter Space and Major Disasters in July 2012. Its contribution includes imagery from the Meteosat and Metop satellites for those disaster activations linked to tropical storms. In addition, it provides access to EUMETCast, a data distribution system, to support the delivery of Charter value added products to users.
EUMETSAT has shared the Lead Agency role with the German Aerospace Centre, Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR) during the period April-October 2018.
Agencia Bolivariana para Activadades Espaciales (ABAE)
Established in 2008 with its headquarters situated in Caracas, Agencia Bolivariana para Actividades Espaciales (ABAE) is a specialised agency in Venezuela responsible for implementing both technical and national policies, as well as guidelines for using outer space for peaceful purposes, emanating from the governing body on science and technology. It is also responsible for generating national space projects, programs and regulations.
ABAE joined the Disasters Charter in 2016 and offers imagery from the two VRSS (Venezuelan Remote Sensing Satellite) missions, Venezuela's first remote sensing satellites.
UAE Space Agency (UAESA) and Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC)
The UAE Space Agency was founded to establish an effective cooperation that contributes to the development of the Arab space sector. The agency aims to drive research and development efforts to achieve the Arab Space Cooperation Group's sustainable space development goals.
The Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) is integral to the strategic initiative put in place by the Dubai government to inspire scientific innovation, technological advancement, and to advance sustainable development in the United Arab Emirates.
UAESA joined the Disasters Charter in 2018 and offers imagery from the DubaiSat-2 mission.


 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French Chinese
Chinese Russian
Russian Portuguese
Portuguese